You can use XPaths to describe where the elements are located on an HTML page.
With ImportFromWeb, you can use XPaths to tell the function what content you want to retrieve from an HTML page
For instance:
=IMPORTFROMWEB("https://nodatanobusiness.com/resources/find-an-xpath-with-little-html-knowledge/", "//title")will output the title of the current article in Google Sheets
XPath is specially useful when the HTML code of a page is rather complex. You don’t necessarily need to learn XPaths to get the most out of ImportFromWeb.
Instead, you can:
- Simply apply the guide “Find an xPath with Google Chrome” in this article
- Start with our ready-to-use solutions
- Use prebuilt selectors
- Use CSS selectors, which are usually simpler to understand
XPaths basics
Let’s start with a basic example of a HTML page.
<html>
<body>
<p>I'm a web page</p>
</body>
</html>We use XPaths to tell a machine what we want to extract from the previous code:
/html/body/pIn that case we indicate the path to the text in the p element, which is the direct child of the body element, which is the direct child of the html element.
Check the result here.
Using IMPORTFROMWEB:
- in our Google Sheet, Let’s paste the few lines of the above code in cell A1
- In A3, let’s type
=IMPORTFROMWEB( A1, "/html/body/p")The expected output in A3 will be
I'm a web page
Ok that’s easy! But a real page is usually more complex. Let’s study two different methods:
- Use Google Chrome
- Write it by yourself
Find an XPath with Google Chrome
This is the easiest method to find the XPath of an element without any knowledge of XPaths:
- Open a page you want to retrieve an element from. Try with https://www.amazon.com/s/?keywords=iphone
- Open the Chrome Developer Tool (⌥⌘I in Mac or F12 with Windows)
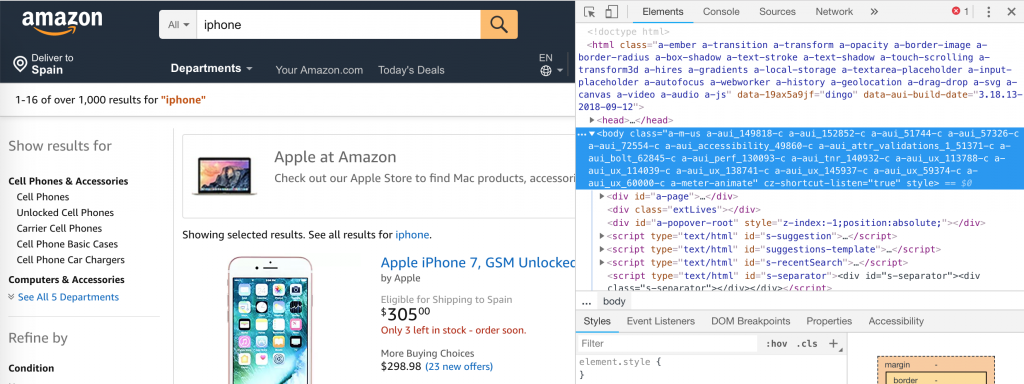
- Click on
 at the top left side of the Chrome Developer Tool
at the top left side of the Chrome Developer Tool - Select an element on the page by clicking on it. The piece of code corresponding to this element should be highlighted.
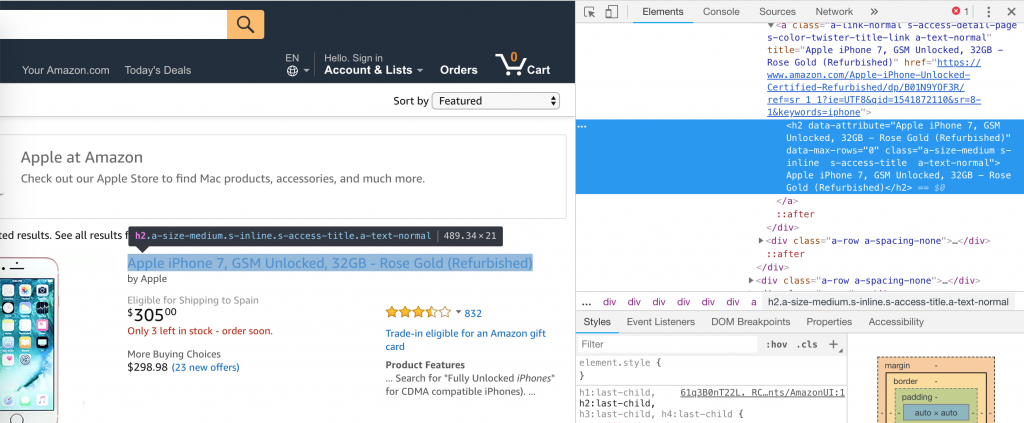
- Right click on the highlighted code and select Copy > Copy XPath
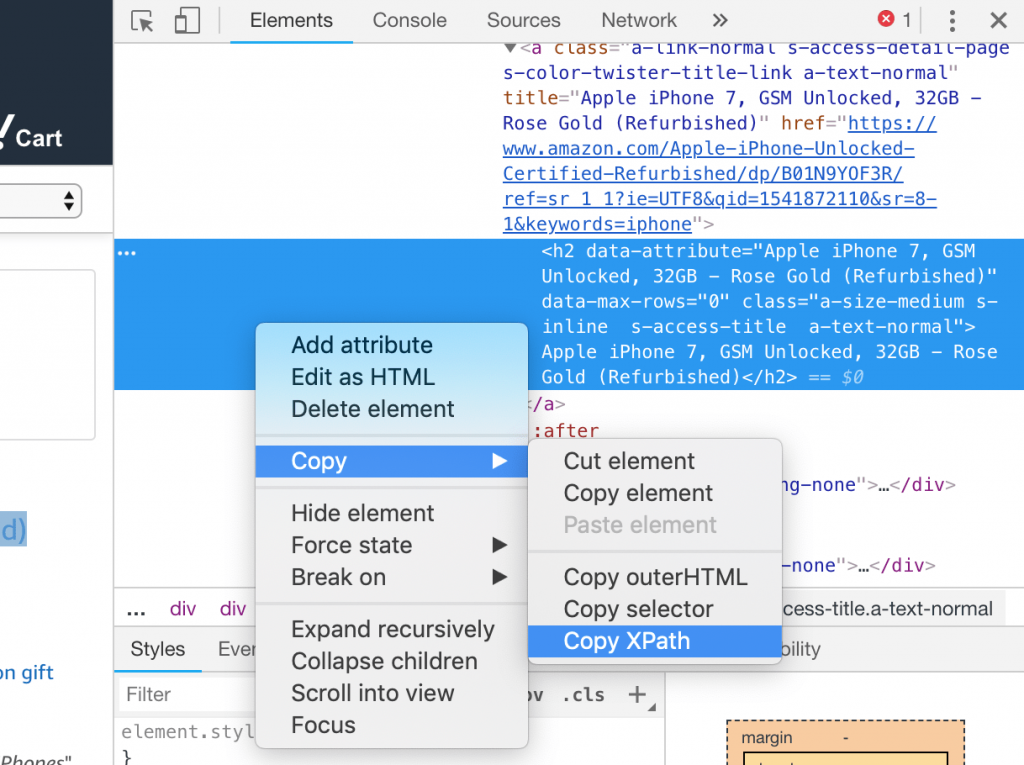
- If you paste it in any document you should see something like
//*[@id="result_0"]/div/div/div/div[2]/div[1]/div[1]/a/h2 Great! We’ve got our XPath.
You can now try this XPath in Google Sheets by using the add-on ImportFromWeb.
Although this method works, the element referenced by this XPath might change if the page is modified. And in a dynamic world, it happens all the time.
By learning how XPaths work you will be able to create XPaths that are less sensitive to changes of the page’s code.
Create your own xPath
While creating your own XPath requires basic HTML knowledge, it is easier than it seems.
Here we’ll reviews the basics to create a solid XPath that can work over many pages that share the same layout.
Let’s start with our previous example, adding a bit of code
<html>
<body>
<p class="paragraph" id="first">I'm a web page</p>
<p class="paragraph" id="second">
Click here to open <a href="https://google.com">Google</a>
</p>
</body>
</html>Absolute path vs. relative path
We saw that we could use /html/body/p to reference the p element, which means listing all the parent element until we get to the element we are looking for.
However an alternative is to call //p to bypass the parents.
Get the Xth element
Using //p would retrieve all the paragraphs. If we want to get only the first one we will use
//p[1]Using attributes
Referencing an element by its attributes offers usually a better way to make a reliable XPath. Then, in our example we could retrieve the first paragraph by using
//p[@id="first"]or even
//p[@class="paragraph"][1]A little note about classes: In general an element can have several classes that can be listed in different orders. the previous XPath assumes that the attribute class looks exactly like paragraph and then would not be valid for something like class="paragraph class2". Hence it’s a good practice to use the following
//p[contains(@class,"paragraph")][1]
Output full element, text or attribute
The previous examples output the HTML element. It is usually more interesting to retrieve only components of that element.
- Output text:
//p[@id="first"]/text()will outputI'm a web page - Output attribute:
//a/@hrefwill outputhttps://google.com
Example
Let’s take our previous example using amazon.com.
By analyzing the code around the search item title, we can see that:
- the parent element with a class “s-item-container” contains all the information relative to a search item
- The title is within an h2 tag
- An a element is parent of the title and has a class “s-access-detail-page”
We can easily create two XPaths that will be very useful:
- Get titles of all search items
//div[contains(@class,"s-item-container")]//h2/text()- Get all the links to the product pages
//div[contains(@class,"s-item-container")]//a[contains(@class,"s-access-detail-page")]/@hrefNow that you know the basics, you can create much more flexible XPaths by using the Rosetta Stone provided by Michael Sorens.
You can play with XPaths by using a Chrome extension like XPather.
